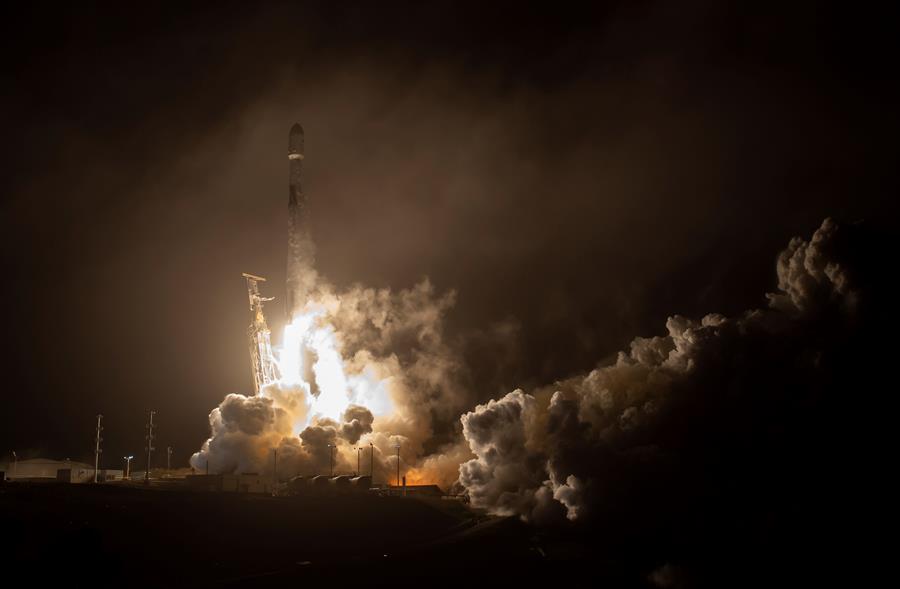
NASA launched a spacecraft that deliberately plans to impact an asteroid in autumn 2022 to deflect its orbit in a test mission that is unprecedented and is part of the strategy of planetary defense of the US Agency Tuesday.
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test mission took off promptly at 10:21 p.m. local time aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Force Base in Vandenberg, California.
This mission has been considered “historic” by NASA since the objective is to collide with an asteroid to divert it from its orbit in order to test the technology that would be necessary to avoid a possible collision with Earth.
The DART spacecraft will head towards the asteroid Didymos and its small moon, Dimorphos, which will be the target of the impact to alter its orbit, which is harmless to Earth.
According to NASA calculations, Didymos and Dimorphos will be relatively close to Earth – about 11 million kilometers – at the estimated time of impact.
Once DART collides with Dimorphos, NASA will examine the changes in its orbit around Didymos to assess whether the method is viable to defend Earth, in case an asteroid poses a threat to the planet in the future.
For the impact to be effective, DART will travel at about 6.6 kilometers per second, an “incredibly fast” speed necessary for the crash to alter “a little” the trajectory of Dimorphos, the size of the George Washington monument – an obelisk. of 155 feet high (47.2 meters) located in the capital of the United States -, but with greater volume, described in an interview with Efe the software engineer at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory Luis Rodríguez, of the team by DART.
The collision will be recorded by a briefcase-sized satellite called CubeSat, which has been developed by the Italian Space Agency.
That cubicle will be deployed shortly before the collision to capture images and videos of the impact and its effects on Dimorphous.
The data from the mission, according to NASA, will be combined with those from the Hera mission, from the European Space Agency and scheduled between 2024 and 2026 to analyze in more detail the asteroids and the crater that DART will leave in Dimorphous.